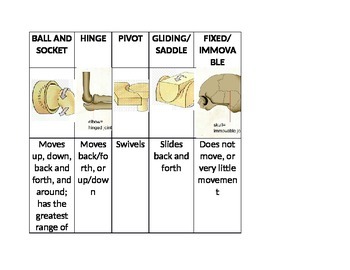
1. Use key responses to identify the joint types described below. Key: a. cartilaginous c; synovial a; cartilaginous b; fibrous a; cartilaginous b; fibrous c; synovial b. fibrous c. synovial 1. includes shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints 2. includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis sutures are memorable examples
Joints.> | Joints in human body, Joints anatomy, Human body lesson plans
The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint ( Figure 38.26 ). These joints can be described as planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, or ball-and-socket joints. Figure 38.26 Different types of joints allow different types of movement. Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of
Source Image: teacherspayteachers.com
Download Image
2,720 solutions More related questions anatomy and physiology Use key responses to identify the joint types described below. Key: a. cartilaginous b. fibrous C. Synovial includes shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis sutures are memorable examples found in the epiphyseal plate

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Hyperextension Joint Injuries to the Knee, Elbow, Shoulder, More Oct 30, 2023Synovial joints are the freely mobile joints in which the articulating surfaces have no direct contact with each other.The movement range is defined (i.e., limited) by the joint capsule, supporting ligaments and muscles that cross the joint. Most of the upper and lower limb joints are synovial.. The majority of the synovial joints are lined with hyaline cartilage, except for the
Source Image: novusspinecenter.com
Download Image
Use Key Responses To Identify The Joint Types
Oct 30, 2023Synovial joints are the freely mobile joints in which the articulating surfaces have no direct contact with each other.The movement range is defined (i.e., limited) by the joint capsule, supporting ligaments and muscles that cross the joint. Most of the upper and lower limb joints are synovial.. The majority of the synovial joints are lined with hyaline cartilage, except for the Use key responses to identify the joint types described below.Key: a. cartilaginous b. fibrous c. synovial1. includes shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints2. includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis 3. sutures are memorable This problem has been solved!
Joint Pain | Novus Spine & Pain Center in Lakeland, Florida
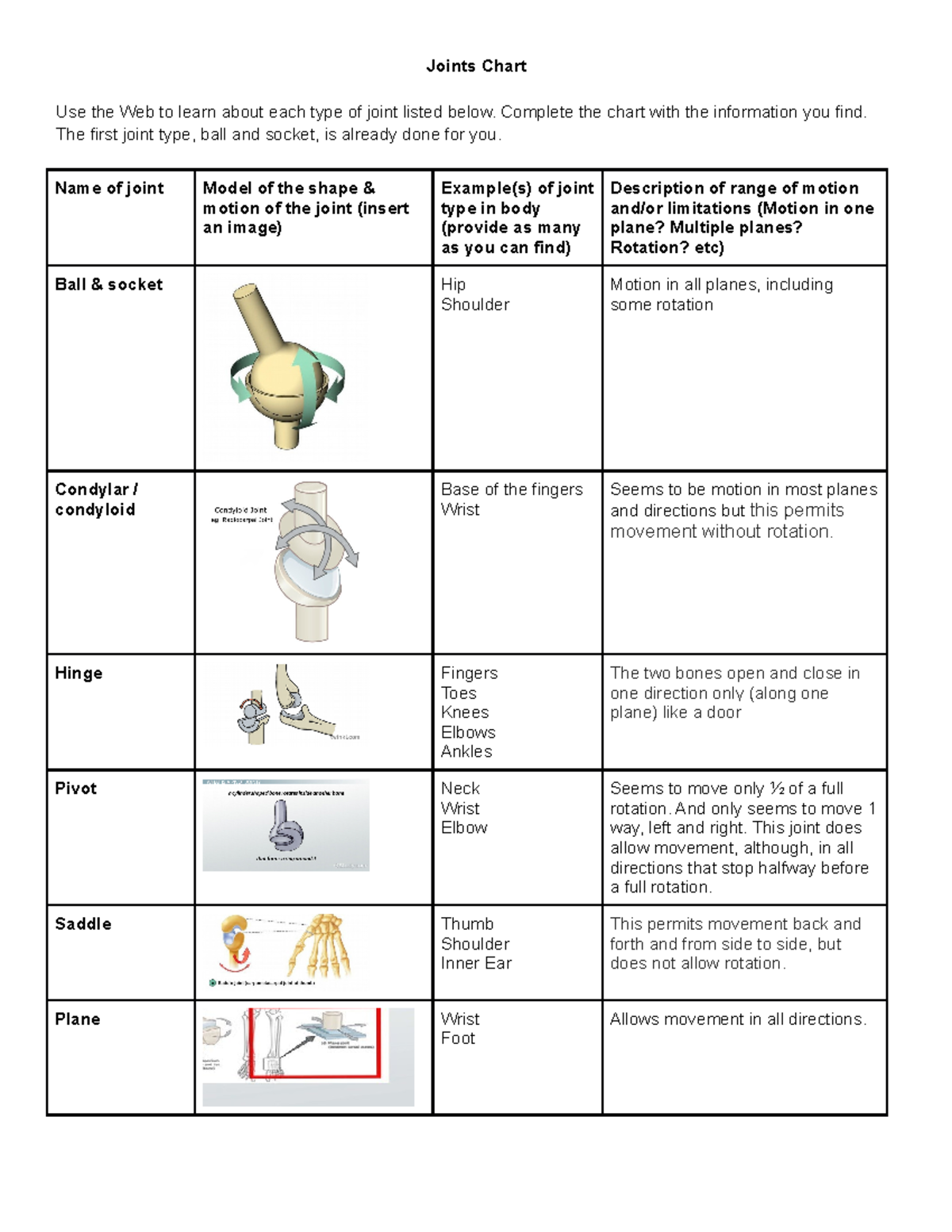
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial Joints I. Use the key to identify the joint types described below. Some responses may be used more than once. … all ch01ce· f , t~ p~ f syno v1al Jom ts. Some responses may be used more than once. ~ – Column A —–+-‘S ~~– 1. joint between skull bones ~'lfo-:: 2. joint between the axis Joints Chart and Labeling – Joints Chart Use the Web to learn about each type of joint listed below. – Studocu
Source Image: studocu.com
Download Image
Stressed vs Unstressed Joint: Top 7 Differences [2024] Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial Joints I. Use the key to identify the joint types described below. Some responses may be used more than once. … all ch01ce· f , t~ p~ f syno v1al Jom ts. Some responses may be used more than once. ~ – Column A —–+-‘S ~~– 1. joint between skull bones ~'lfo-:: 2. joint between the axis
![Stressed vs Unstressed Joint: Top 7 Differences [2024]](https://woodworkly.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Stressed-vs-Unstressed-joint.webp)
Source Image: woodworkly.com
Download Image
Joints.> | Joints in human body, Joints anatomy, Human body lesson plans 1. Use key responses to identify the joint types described below. Key: a. cartilaginous c; synovial a; cartilaginous b; fibrous a; cartilaginous b; fibrous c; synovial b. fibrous c. synovial 1. includes shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints 2. includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis sutures are memorable examples
 Download Image
Download ImageHyperextension Joint Injuries to the Knee, Elbow, Shoulder, More 2,720 solutions More related questions anatomy and physiology Use key responses to identify the joint types described below. Key: a. cartilaginous b. fibrous C. Synovial includes shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis sutures are memorable examples found in the epiphyseal plate

Source Image: healthline.com
Download Image
How Many Joints in the Human Body: Types of Joints, Variables & More Synovial. A synovial joint is defined by the presence of a fluid-filled joint cavity contained within a fibrous capsule.. They are freely movable (diarthrosis) and are the most common type of joint found in the body. Synovial joints can be sub-classified into several different types, depending on the shape of their articular surfaces and the movements permitted:

Source Image: healthline.com
Download Image
How Many Joints in the Human Body: Types of Joints, Variables & More Oct 30, 2023Synovial joints are the freely mobile joints in which the articulating surfaces have no direct contact with each other.The movement range is defined (i.e., limited) by the joint capsule, supporting ligaments and muscles that cross the joint. Most of the upper and lower limb joints are synovial.. The majority of the synovial joints are lined with hyaline cartilage, except for the

Source Image: healthline.com
Download Image
Static and Dynamic Stretching: Tips for Athletes | HSS Use key responses to identify the joint types described below.Key: a. cartilaginous b. fibrous c. synovial1. includes shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints2. includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis 3. sutures are memorable This problem has been solved!

Source Image: hss.edu
Download Image
Stressed vs Unstressed Joint: Top 7 Differences [2024]
Static and Dynamic Stretching: Tips for Athletes | HSS The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint ( Figure 38.26 ). These joints can be described as planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, or ball-and-socket joints. Figure 38.26 Different types of joints allow different types of movement. Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of
Hyperextension Joint Injuries to the Knee, Elbow, Shoulder, More How Many Joints in the Human Body: Types of Joints, Variables & More Synovial. A synovial joint is defined by the presence of a fluid-filled joint cavity contained within a fibrous capsule.. They are freely movable (diarthrosis) and are the most common type of joint found in the body. Synovial joints can be sub-classified into several different types, depending on the shape of their articular surfaces and the movements permitted: