Jul 12, 2023With one filled π bonding orbital holding three atoms together, the net π bond order is ½ per O-O bond. The combined σ / π bond order is thus 1½) for each O-O bond. We can now place the remaining four electrons in the three energy levels shown in Figure 11.6.7, thereby filling the π bonding and the nonbonding levels.
nanoGe – Our speakers
Use resonance structures to show how its double bond is delocalized. Answer. Exercise 13.14.2 13.14. 2. Use resonance structures to show that the negative charge in a formate ion (HCO 2-, C is in the middle and attached to the three other atoms) is spread out (delocalized) over more than one oxygen atom. Answer.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
bond order = numberof bonding electrons − number of antibonding electrons 2. To calculate the bond order of H 2, we see from Figure 6.5.2 that the σ 1s (bonding) molecular orbital contains two electrons, while the σ ⋆ 1s (antibonding) molecular orbital is empty. The bond order of H 2 is therefore.
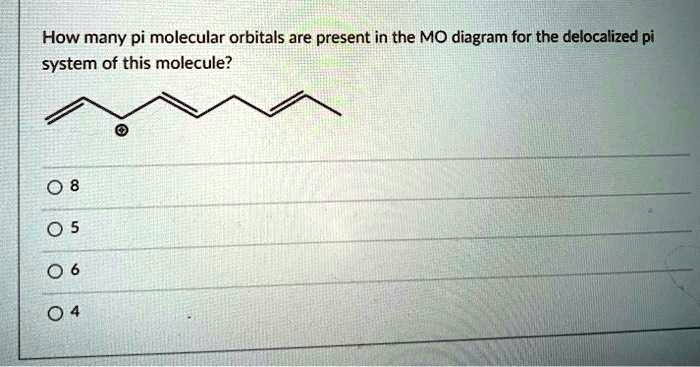
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Which of the statements about 1,3-butadiene is correct? There are two separate double bonds in 1,3-butadiene; and each has two pi molecular orbitals which contain the electrons. There are four pi Jun 19, 2023The species that contains a delocalized π bond is Benzene, C6H6. This is because the electrons in the π bond are spread out over all of the six carbon atoms in the benzene ring, making it a delocalized π bond rather than a localized π bond. The delocalization of the π electrons stabilizes the molecule, making it more difficult to break apart.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Which Of The Species Contains A Delocalized π Bond
Jun 19, 2023The species that contains a delocalized π bond is Benzene, C6H6. This is because the electrons in the π bond are spread out over all of the six carbon atoms in the benzene ring, making it a delocalized π bond rather than a localized π bond. The delocalization of the π electrons stabilizes the molecule, making it more difficult to break apart. NO3 delocalized bonds are present in a molecule that has resonance structures. MO theory is better at describing _____ than VB theory. … nodes, what is the expected bond order for the diatomic species B2? and more. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like bonding orbitals, nodes, what is the expected bond order for
SOLVED: (a) What is Huckel theory? Why is it used? What assumptions does it make? (b) Consider hexatriene. How many molecular orbitals would you expect there to be? Write the secular determinant
Jan 30, 2023Delocalization, Conjugated Systems, and Resonance Energy. The presence of alternating π π and σ σ bonds in a molecule such as benzene is known as a conjugated system, or conjugated π π bonds. Conjugated systems can extend across the entire molecule, as in benzene, or they can comprise only part of a molecule. SOLVED: Q2 (a) [25 Marks] A molecule with 5 electrons in the delocalized molecular orbitals (MO) has the following secular matrix when applying the Huckel MO theory assumptions: a-E B a-E 0
![SOLVED: Q2 (a) [25 Marks] A molecule with 5 electrons in the delocalized molecular orbitals (MO) has the following secular matrix when applying the Huckel MO theory assumptions: a-E B a-E 0](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/ba0622afbd3841aaab04770deb571745.jpg)
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Which of the following compounds have delocalized electrons? Provide resonance contributors for the compounds that have delocalized electrons. 1. CH2=CH-CH=CH-CH2 2. CH2=CH-CH=CH 3. CH2-CH=N-CH=CH 4. CH2-NH-CH=CH Jan 30, 2023Delocalization, Conjugated Systems, and Resonance Energy. The presence of alternating π π and σ σ bonds in a molecule such as benzene is known as a conjugated system, or conjugated π π bonds. Conjugated systems can extend across the entire molecule, as in benzene, or they can comprise only part of a molecule.
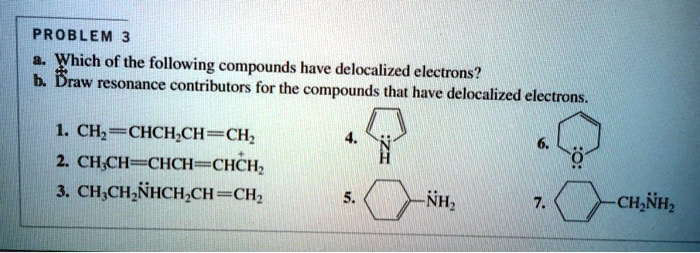
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
nanoGe – Our speakers Jul 12, 2023With one filled π bonding orbital holding three atoms together, the net π bond order is ½ per O-O bond. The combined σ / π bond order is thus 1½) for each O-O bond. We can now place the remaining four electrons in the three energy levels shown in Figure 11.6.7, thereby filling the π bonding and the nonbonding levels.
Source Image: nanoge.org
Download Image
SOLVED: Which of the statements about 1,3-butadiene is correct? There are two separate double bonds in 1,3-butadiene; and each has two pi molecular orbitals which contain the electrons. There are four pi bond order = numberof bonding electrons − number of antibonding electrons 2. To calculate the bond order of H 2, we see from Figure 6.5.2 that the σ 1s (bonding) molecular orbital contains two electrons, while the σ ⋆ 1s (antibonding) molecular orbital is empty. The bond order of H 2 is therefore.
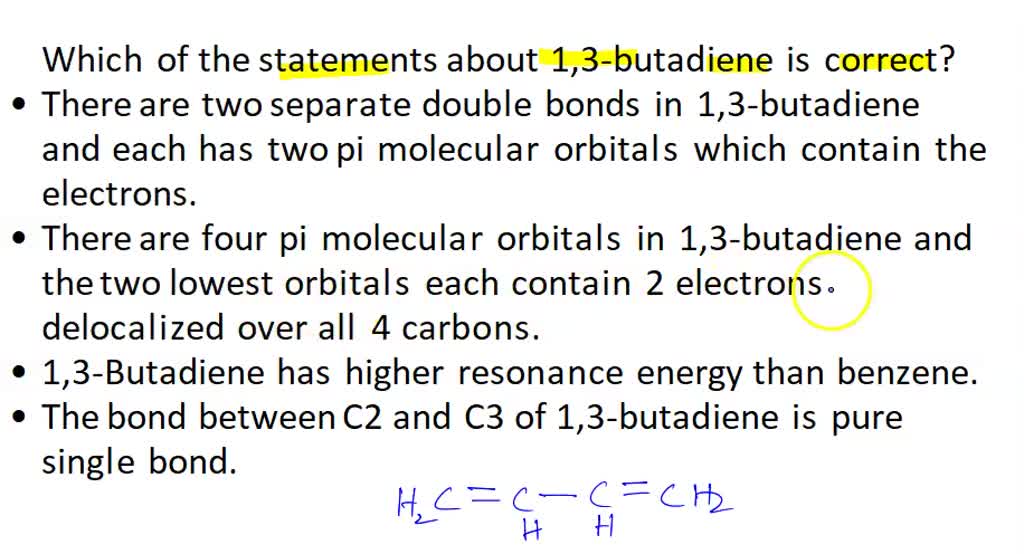
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
1. chemical bond: -ionic bond: 4. Types of Bonds: -covalent bond: – ppt download Ernest Z. Nov 20, 2016 A delocalized π bond is a π bond in which the electrons are free to move over more than two nuclei. Explanation: In a molecule like ethylene, the electrons in the π bond are constrained to the region between the two carbon atoms. We say that the π electrons are localized.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
A bond bundle case study of Diels-Alder catalysis using oriented electric fields – ScienceDirect Jun 19, 2023The species that contains a delocalized π bond is Benzene, C6H6. This is because the electrons in the π bond are spread out over all of the six carbon atoms in the benzene ring, making it a delocalized π bond rather than a localized π bond. The delocalization of the π electrons stabilizes the molecule, making it more difficult to break apart.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Halogen Bonding in Sulphonamide Co-Crystals: X···π Preferred over X···O/N? NO3 delocalized bonds are present in a molecule that has resonance structures. MO theory is better at describing _____ than VB theory. … nodes, what is the expected bond order for the diatomic species B2? and more. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like bonding orbitals, nodes, what is the expected bond order for
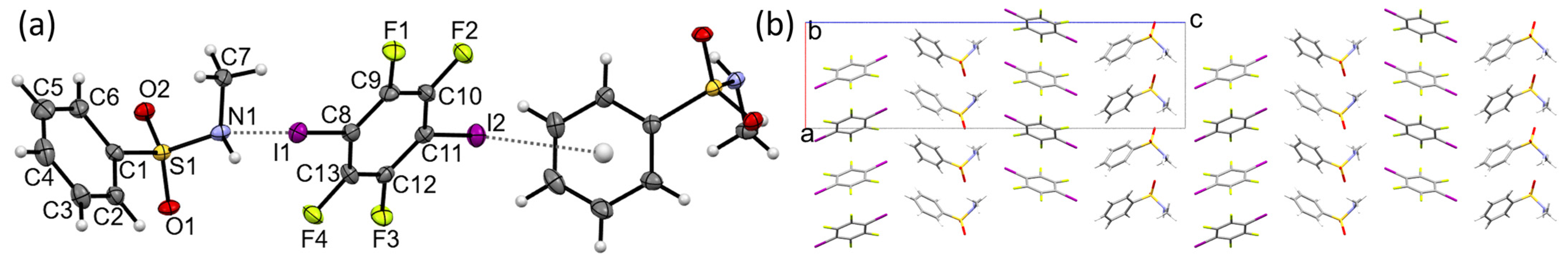
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Which of the following compounds have delocalized electrons? Provide resonance contributors for the compounds that have delocalized electrons. 1. CH2=CH-CH=CH-CH2 2. CH2=CH-CH=CH 3. CH2-CH=N-CH=CH 4. CH2-NH-CH=CH
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Halogen Bonding in Sulphonamide Co-Crystals: X···π Preferred over X···O/N? Use resonance structures to show how its double bond is delocalized. Answer. Exercise 13.14.2 13.14. 2. Use resonance structures to show that the negative charge in a formate ion (HCO 2-, C is in the middle and attached to the three other atoms) is spread out (delocalized) over more than one oxygen atom. Answer.
SOLVED: Which of the statements about 1,3-butadiene is correct? There are two separate double bonds in 1,3-butadiene; and each has two pi molecular orbitals which contain the electrons. There are four pi A bond bundle case study of Diels-Alder catalysis using oriented electric fields – ScienceDirect Ernest Z. Nov 20, 2016 A delocalized π bond is a π bond in which the electrons are free to move over more than two nuclei. Explanation: In a molecule like ethylene, the electrons in the π bond are constrained to the region between the two carbon atoms. We say that the π electrons are localized.